17.2.1 Relationships with regional NGOs and government for SDG policy
NTNU actively collaborates with government agencies and non-governmental organizations to advance policy research and practices related to sustainable development. Key initiatives in 2024 include:
1. National Program for Deepening Adapted Physical Education in Schools
The Center for Adapted Physical Education at NTNU was commissioned by the Sports Administration, Ministry of Education, to lead the 2024 National Program for Deepening Adapted Physical Education in Schools, in collaboration with three other universities. As the lead institution, NTNU is responsible for drafting the Policy Recommendations for the Sustainable Development of Adapted Physical Education, as well as overseeing overall program monitoring, evaluation, and guidance.
The policy report identified several challenges in Taiwan’s implementation of adapted physical education, including insufficient cross-ministerial collaboration, inconsistency in policy execution, inadequate professional teacher training, and limited accessibility and inclusiveness of school sports facilities and adaptive equipment. To address these issues, the report proposed strategies to strengthen cross-ministerial cooperation, clarify division of responsibilities, and enhance integrated governance, with the aim of improving policy effectiveness and long-term sustainability.
Subproject teams focused on promoting adapted physical education across all school levels nationwide, providing professional development for teachers, and assisting schools and local governments in sports facility planning and adaptive equipment allocation.

2. Policy Recommendations on Education for Middle-Aged and Older Adults
The Higher Education Sprout Project Office and the NTNU Education Think Tank co-organized the Policy Forum on Education for Middle-Aged and Older Adults on April 2, 2024, bringing together nearly 100 scholars, experts, faculty, students, and members of the public. The forum facilitated in-depth academic discussions on Taiwan’s current policy responses and future strategic directions regarding education for middle-aged and older adults.
Subsequently, on August 12, 2024, NTNU officially released the Policy Recommendations on Education for Middle-Aged and Older Adults. The report examined Taiwan’s current status and challenges across five key dimensions—government resource integration; education and career transition for middle-aged and older adults; social connectedness and intergenerational interaction; independent living skills; and mental health and meaning of life—and proposed corresponding policy recommendations. It called on the government to integrate lifelong learning into the daily lives of middle-aged and older adults at an early stage, enabling them to develop autonomy and independence, maintain physical and mental well-being, and foster healthy social connections.

Policy Forum on Education for Middle-Aged and Older Adults
These initiatives demonstrate NTNU’s active role in advancing national sustainability policies. Through policy innovation and cross-sector collaboration, the university contributes to the achievement of SDG 3, SDG 4, and SDG 10.
17.2.2 Cross sectoral dialogue about SDGs
NTNU actively promotes and participates in cross-sectoral dialogue on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), fostering collaboration among government agencies, non-governmental organizations, industry, and academia through diverse engagement platforms. Key initiatives in 2024 include:
1. Post-COP29 Climate Change and Corporate Sustainability Trends Symposium
- Participants: Ministry of Environment, ASUS, Delta Electronics, British Standards Institution, Cathay Financial Holdings, and representatives from government, industry, and academia.
- Discussion Topics: Climate finance, renewable energy transition, climate risk management, and public–private collaboration to foster cross-sector engagement in developing sustainability strategies and carbon reduction actions.

2. 2024 Gifted Education Resource Center Exchange Meeting
- Participants: Keelung City Government Education Department, Jian De Primary School, Keelung Resource Center for Gifted and Talented, Division of Special Education (New Taipei City Government), and New Taipei City Gifted and Talented Education Resource Center.
- Discussion Topics: Challenges in gifted education policies and implementation, discussed from the perspectives of teacher training universities, local governments, gifted education resource centers, and frontline teachers to enhance experience sharing, professional learning, and resource integration.

Through these cross-sectoral exchanges, NTNU demonstrates its commitment to SDG collaboration, contributing to SDG4, SDG13, and SDG17.
17.2.3 International collaboration data gathering for SDG
Professor Yu-Feng Hsu of the Department of Life Science at NTNU contributed to an international research project, the findings of which were published in Nature Ecology & Evolution under the title “A global phylogeny of butterflies reveals their evolutionary history, ancestral hosts and biogeographic origins” (DOI: 10.1038/s41559-023-02041-9).
This large-scale global research effort involved sequencing 391 genes from nearly 2,300 butterfly species, with samples collected from 90 countries and 28 specimen collections worldwide. The study reconstructed a comprehensive phylogenomic tree representing 92% of all butterfly genera, forming one of the most complete biodiversity datasets to date.
The study revealed that butterflies originated in the Americas around 100 million years ago, initially feeding on Fabaceae (legume) plants, and gradually dispersed worldwide after the Cretaceous Thermal Maximum. The molecular, host plant, and geographic data provided by this research established an important foundation for future comparative evolutionary studies of butterflies, contributing to the advancement of SDG 15 (Life on Land).
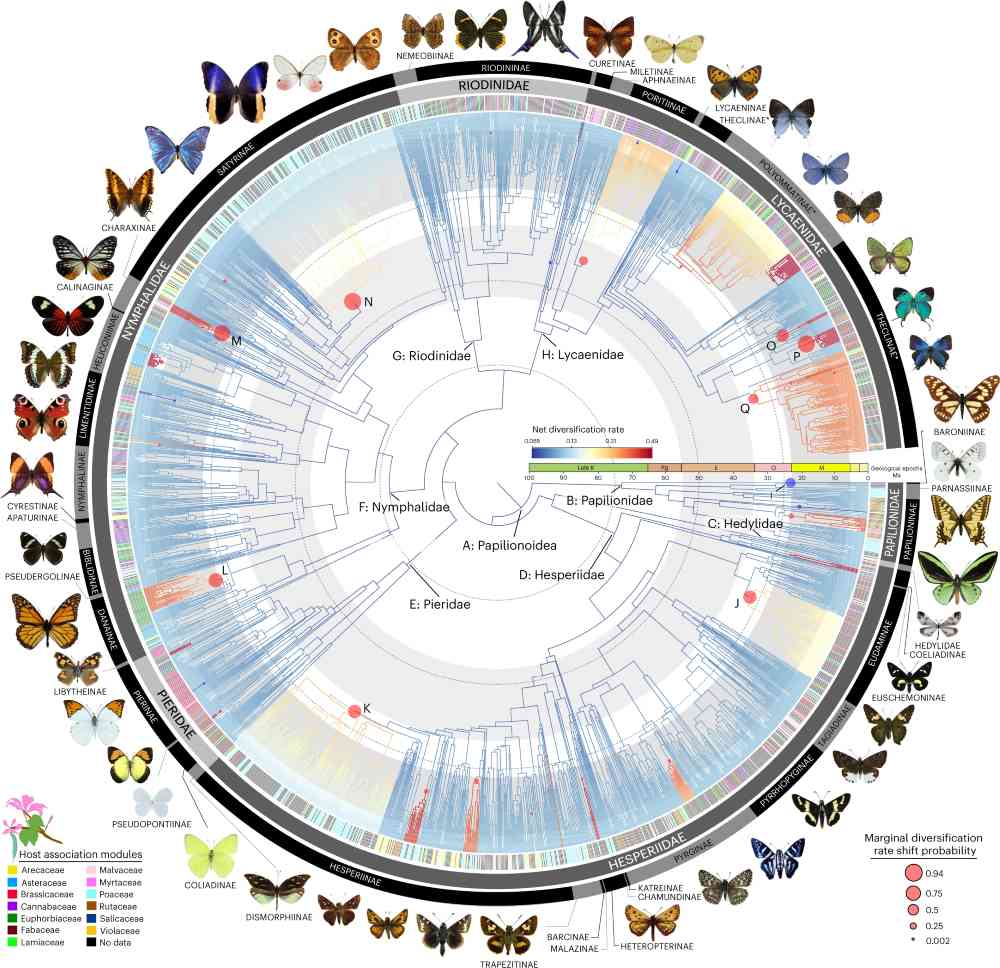
Evolutionary relationships and diversification patterns of butterflies
Source: A global phylogeny of butterflies reveals their evolutionary history, ancestral hosts and biogeographic origins
17.2.4 Collaboration for SDG best practice
The University actively engages in international research, collaboration, and best practice exchange related to SDGs. Key initiatives in 2024 include:
1. 2024 International Camp of Smart & Sustainable Textiles
- Partners: Scholars, government representatives, and industry leaders from Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, and the Philippines, as well as the Sustainable Consumption and Production Association (Thailand Chapter).
- Discussion Topics: The program centered on green textiles, circular economy, AI-enabled recycling systems, carbon-neutral supply chains, and smart textile innovation. Through keynote lectures, hands-on workshops, and industrial visits, the camp facilitated knowledge exchange and promoted innovative models for sustainable textile development.

2. APERA 2024 International Conference
- Partners: Education scholars from 12 countries, including Taiwan, Japan, Thailand, Singapore, the Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, Indonesia, South Korea, the United Kingdom, China, and Australia.
- Discussion Topics: The conference, themed “Interdisciplinary Research and Practice in Teacher Education,” explored topics such as education for sustainable development, educational technology innovation, special education teacher preparation, and the application of AI in educational practice.

Through these international collaborations and research exchanges, the University continues to strengthen global partnerships with academic and industry stakeholders, enhance the exchange of sustainability knowledge and practices, and contribute to SDG4, SDG9, SDG12, and SDG17.
17.2.5 Collaboration with NGOs for SDGs
NTNU actively collaborates with NGOs through student volunteering programmes, research programmes, and the development of educational resources to jointly advance SDGs. The key achievements in 2024 are as follows:
1. Research Programme
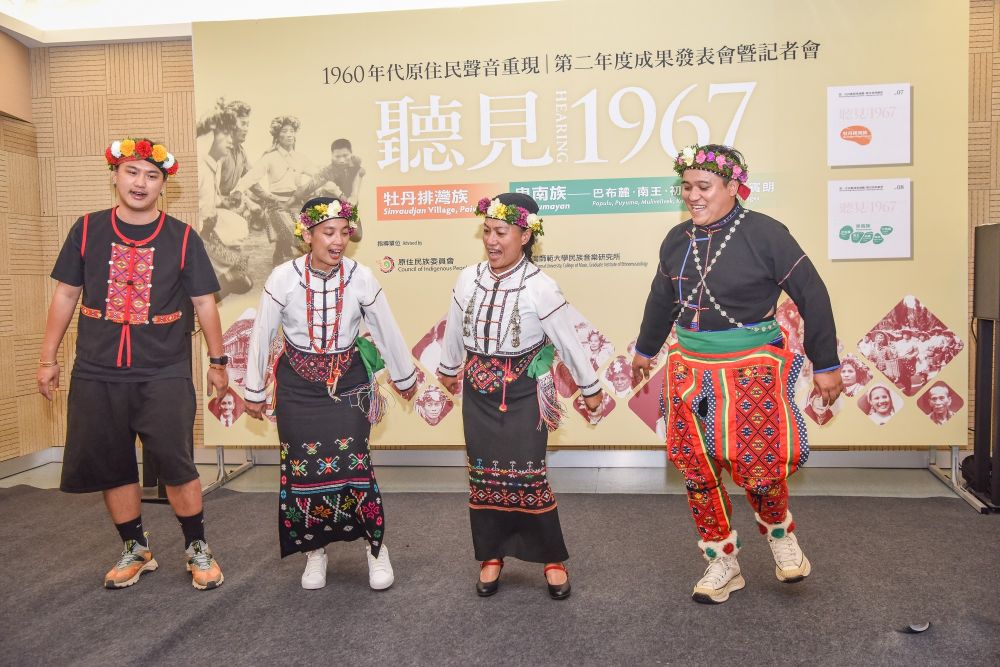
- Indigenous Sound Reappearance Publication Project (1960s Archival Collection)
In 2013, NTNU obtained rare recordings from the 1967 Taiwan Folk Song Collection Movement through collaboration with a scholar from the The Institute of Oriental and Asian Studies, University of Bonn’s in Germany. NTNU subsequently partnered with the Council of Indigenous Peoples and Indigenous communities to launch the “Indigenous Sound Reappearance Publication Project.” The research team carried out the digitization of historical recordings, lyric transcription, archival research, and field investigations, and in 2024 published two albums featuring the Paiwan and Puyuma peoples.
The team also returned the audio archives to the communities for collaborative interpretation and revitalization of traditional singing practices. NTNU further worked with local schools to help children learn Indigenous songs, promoting cultural preservation, intergenerational transmission, and mother tongue revitalization—contributing to SDG 4, SDG 11, and SDG 17.

2. Student Volunteering Programme
- International Chinese Language Tutoring Volunteer Program
Since 2023, NTNU has collaborated with the Tzu Chi Foundation to implement the “Promise of Manaheim” Chinese Tutoring Program for Syrian Refugees, training international Mandarin teaching volunteers to provide language-learning support for Syrian refugee students.
In 2024, the program expanded into the “International Chinese Language Tutoring Volunteer Program,” extending services to underprivileged children in Northern Thailand. Over 70 student volunteers have been selected and trained using NTNU-developed digital teaching platforms. Since May 2024, volunteers have provided weekly online tutoring and conducted Chinese language camps in Türkiye and Thailand during the 2024 summer and 2025 winter breaks.
Through this partnership, NTNU and the Tzu Chi Foundation jointly promote educational equity, cross-cultural exchange, and student social engagement, advancing SDG 4 and SDG 10.

- Student Community Service Teams
NTNU student clubs regularly engage in nationwide community service during winter and summer breaks, spreading care and support across Taiwan. In 2024, a total of 48 student service teams were deployed, covering: Northern Taiwan (25 teams), Central Taiwan (8), Southern Taiwan (7), Eastern Taiwan (5), Offshore Islands (1), and two teams providing island-wide mobile services.

3. Development of Educational Resources
- “Taiwan Hearts Connecting the New Generation” Project
NTNU implements the “Taiwan Hearts Connecting the New Generation” project using two self-developed digital learning platforms—SmartZhuyin and eMPOWER Mandarin Learning Platform—to enhance the Mandarin proficiency of children from new immigrant families and promote equitable access to education.
In 2024, the project supported students from 45 countries across 215 primary and secondary schools, reaching over 40,000 learners. Approximately 80% of participating students improved by one level on the TOCFL Mandarin Proficiency Test within one semester. This initiative addresses linguistic inequality faced by new immigrant children, supports their education and social inclusion, and contributes to SDG 1, SDG 4, and SDG 10.

17.4.1 Education for SDGs commitment to meaningful education
NTNU is committed to integrating the SDGs into its university-wide curriculum to ensure that sustainability education is meaningful and relevant to all students.
The Office of Academic Affairs encourages faculty members to reflect on how their courses align with the SDGs when designing syllabi. Instructors can indicate the SDG targets related to their course content when submitting course outlines, thereby fostering awareness of sustainability across all disciplines.
In the 2023 academic year, a total of 1,833 courses were identified by instructors as being related to one or more SDGs. NTNU offered a wide range of SDG-related courses, including 1,360 courses linked to SDG 4 (Quality Education), 636 to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), 522 to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), and numerous others spanning all 17 SDGs, demonstrating NTNU’s strong commitment to embedding sustainability education throughout the entire curriculum.
Goals | Number of Course |
SDG1 | 93 |
SDG2 | 63 |
SDG3 | 636 |
SDG4 | 1360 |
SDG5 | 460 |
SDG6 | 83 |
SDG7 | 155 |
SDG8 | 522 |
SDG9 | 263 |
SDG10 | 430 |
SDG11 | 264 |
SDG12 | 159 |
SDG13 | 160 |
SDG14 | 105 |
SDG15 | 107 |
SDG16 | 449 |
SDG17 | 240 |
17.4.2 Education for SDGs specific courses on sustainability
NTNU offers a wide range of degree programs and elective courses dedicated to SDGs. These courses cover sustainability knowledge, competencies, and practical applications, enabling students to develop the capacity to take action across diverse fields.
1. Graduate Institute of Sustainability Management and Environmental Education
The Graduate Institute of Sustainability Management and Environmental Education (GISMEE) combines the dual focuses of sustainability development and environmental education, fostering professionals with sustainability governance perspectives, scientific literacy, and cross-disciplinary practical skills. The faculty’s expertise spans environmental science, sustainability management, ecosystem studies, climate change adaptation, outdoor and environmental education, environmental communication, citizen science, and local sustainable development. The institute emphasizes a balance between theory and practice, international engagement, and local implementation.
GISMEE is structured around two divisions — Sustainability Management and Environmental Education — both designed to integrate knowledge across disciplines and connect academic research with practical application.
- Sustainability Management Division:
Core courses include Research on Sustainability Management, with electives such as Resource Recycling and Waste Management, Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation, Carbon Management, Sustainable Finance, Exploration of Emerging Corporate Sustainability Issues, and Sustainable Marketing and Brand Management.
- Environmental Education Division:
Core courses include Studies in Environmental Education, complemented by electives such as Theory and Practice of Environmental Learning Centers, Qualitative Research in Environmental Education, Community Environmental Education, Environmental Interpretation, Environmental Education in Museums, and Disaster Prevention Education. These courses combine theoretical foundations with field-based learning and social engagement.
Overall, the institute’s curriculum emphasizes interdisciplinary integration and alignment with global sustainability trends, covering key topics such as climate change, resource management, sustainable finance, carbon neutrality policies, and applied environmental education. The program nurtures students with both leadership in sustainability and practical competencies for real-world application.
The Course Structure of GISMEE is as follows:
2. Department of Geography
- Environmental Monitoring and Disaster Prevention Program
This program integrates resources from geography, earth sciences, life sciences, and environmental education to cultivate students’ abilities in environmental monitoring, disaster prevention planning, and environmental management. The curriculum includes Natural Disasters, Environmental Impact Assessment, Landscape Survey and Analysis, and Disaster Management and Prevention Practice, emphasizing fieldwork, data analysis, and hands-on research. Students gain professional skills in environmental monitoring, data processing, and environmental assessment.
- Regional and Tourism Planning Program
Based on the foundations of geography, this program integrates three major areas — regional planning, tourism development, and land-use regulations — to equip students with practical skills in regional management and sustainable local development. The courses include Resource and Regional Planning, Environmental Planning and Design, Land Laws and Regulations, and Urban and Regional Planning. The program also collaborates with government agencies such as the Construction and Planning Agency, Tourism Bureau, and local governments, as well as partner universities, enabling students to bridge academic theory and policy practice. It strengthens professional ethics in sustainable land development and enhances expertise in regional and tourism planning for sustainable communities.
The course lists for the two programs are as follows:
17.4.3 Education for SDGs in the wider community
NTNU’s University Social Responsibility (USR) teams actively promote diverse and systematic community outreach and educational services. The beneficiaries include alumni (school teachers), community residents, international refugees, older adults, new immigrants, and second-generation immigrant children, with the aim of enhancing learning opportunities and supporting physical and mental well-being. The key USR initiatives in 2024 are as follows:
1. Rural Education Empowerment Program
- Beneficiaries: Students and teachers in rural schools; Syrian refugees
- Overview & Outcomes: NTNU developed the PASSION teaching model to improve teaching quality in rural areas, addressing teacher turnover and resource disparities. The project has served 98,782 students, offered 1,873 classes, and provided capacity-building for 4,471 teachers. International outreach extended support to Syrian refugee children and ethnic Chinese students in Northern Thailand, delivering a total of 36,308 teaching hours.
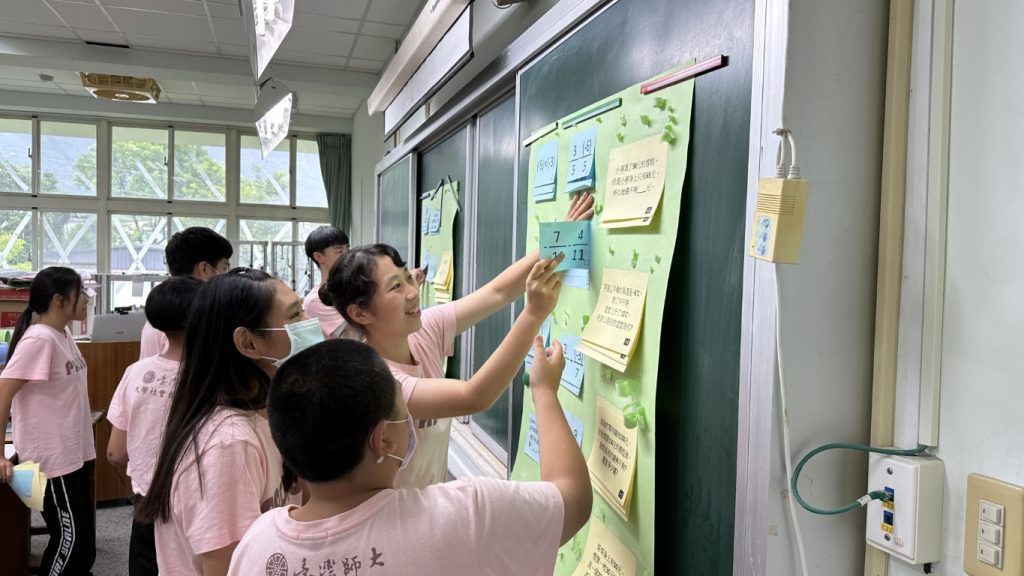
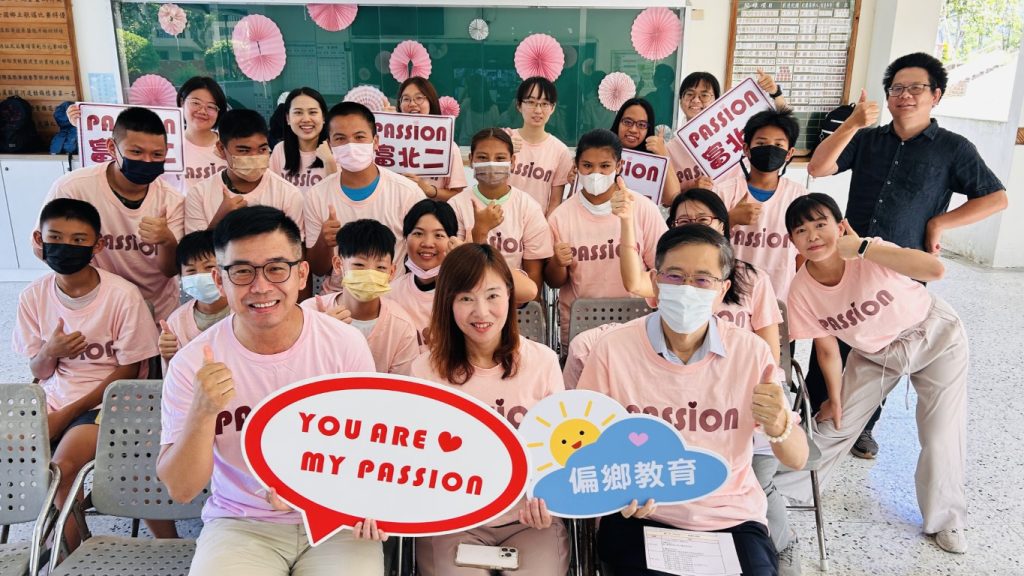


The PASSION teaching team from NTNU provided services to teachers and students in rural schools.
2. Digital Inclusion and Smart Active Aging Program
- Beneficiaries: Older adults in local communities
- Overview & Outcomes: In collaboration with communities and industry partners, the program promotes digital inclusion and health management for seniors through health-tech screening, wellness courses, and intergenerational learning. In 2024, it organized 36 health-tech promotion activities, 261 wellness and intergenerational courses, and 51 digital inclusion sessions, with a total of 14,378 participants.
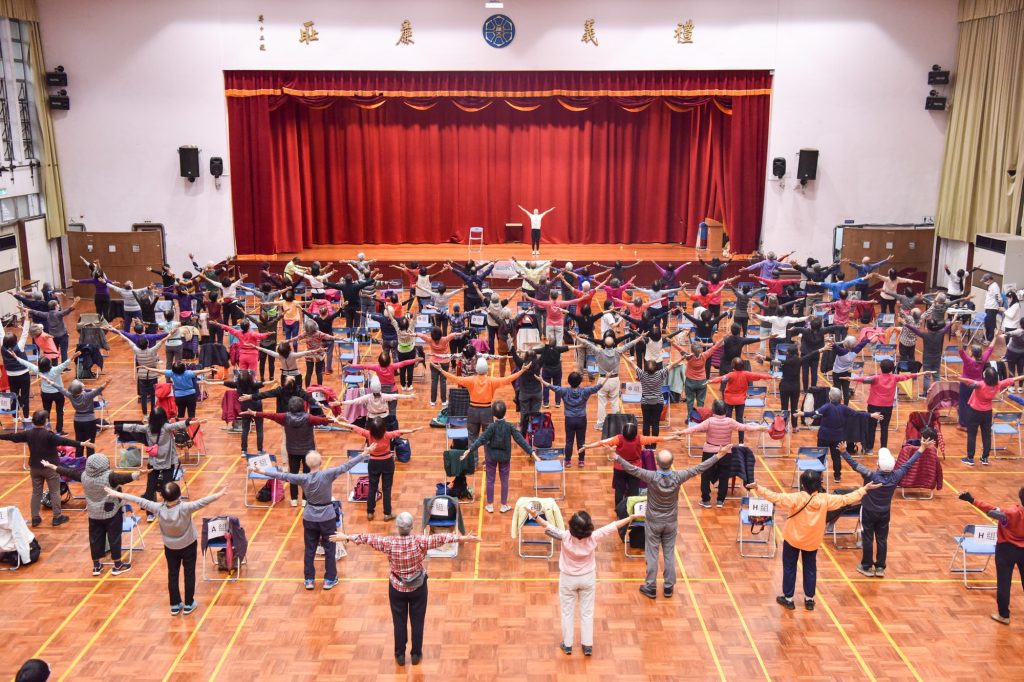
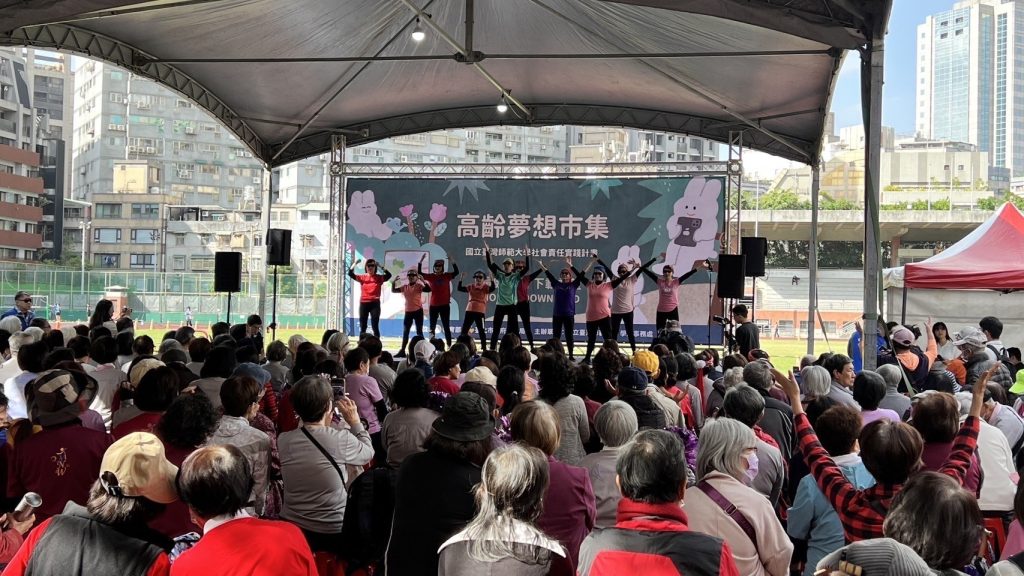


The project team organized various physical and mental well-being activities for older adults.
3. Taiwan Hearts Connecting the New Generation
- Beneficiaries: New immigrants and second-generation immigrant children
- Overview & Outcomes: Using two NTNU-developed digital Mandarin learning platforms, the project supports students from 45 countries and 215 schools. In 2024, it benefited 40,000 learners, with 80% improving by one level on the TOCFL Mandarin proficiency test in a single semester.

4. Warm Sun Community Mental Wellness Program
- Beneficiaries: Economically disadvantaged older adults and their families
- Overview & Outcomes: In partnership with NTNU’s Counseling Center and social welfare organizations, the program provides free counseling, mental health workshops, stress-relief activities, and meal support services. In 2024, the program served 483 individuals.

5. Rural Science Education Initiative
- Beneficiaries: Students and teachers in rural schools
- Overview & Outcomes: This initiative conducts hands-on science workshops to strengthen scientific inquiry and experiment-based learning in rural areas. In 2024, it held 49 workshops, benefiting 14,512 participants.

Through these USR programs, NTNU continues to promote educational equity, deepen engagement with local communities, and support older adults and disadvantaged groups. These initiatives exemplify the university’s social responsibility and directly contribute to SDG 1, SDG 3, SDG 4, SDG 10, SDG 11, and SDG 17.
17.4.4 Sustainable Literacy
Since 2021, the NTNU Center for Sustainable Development has conducted the annual Sustainability Literacy Survey during major campus events such as freshman orientation and the “Sustainable Warm Day Festival.” The survey systematically measures faculty, staff, and students’ understanding and actions related to sustainability and net-zero issues. It assesses three key dimensions—knowledge, attitudes, and behavioral participation—to evaluate the effectiveness of sustainability education at the university.
In the 2024 survey, approximately 50% of respondents were students, 20% were faculty and staff, and 30% were external participants. Based on a ten-point scale, the median score was six, indicating a moderate level of understanding of sustainability topics. However, respondents showed lower familiarity with net-zero issues such as the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). Additionally, about 20% of respondents reported not regularly carrying reusable cups, while another 20% indicated that they brought their own containers more than ten times when purchasing beverages—highlighting room for improvement in sustainable lifestyle habits.
This annual survey not only helps NTNU assess the current level of sustainability literacy among its campus community but also serves as an important foundation for designing future educational initiatives and strengthening sustainability awareness across the university.



